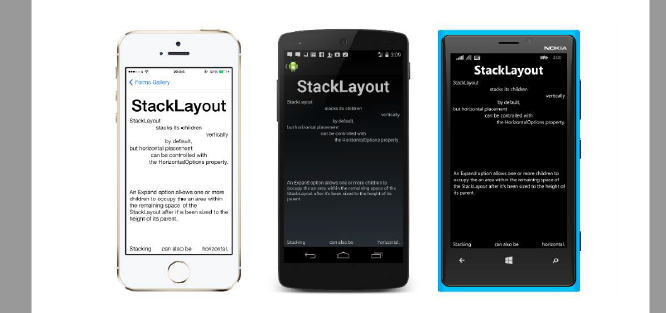
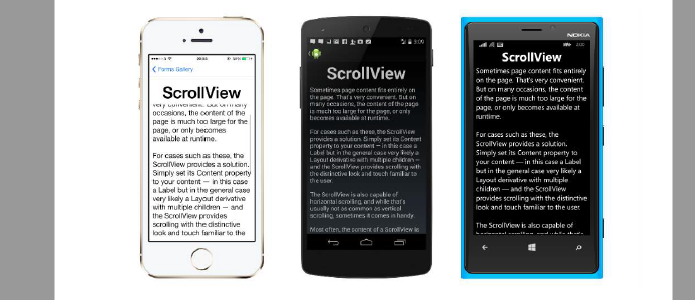
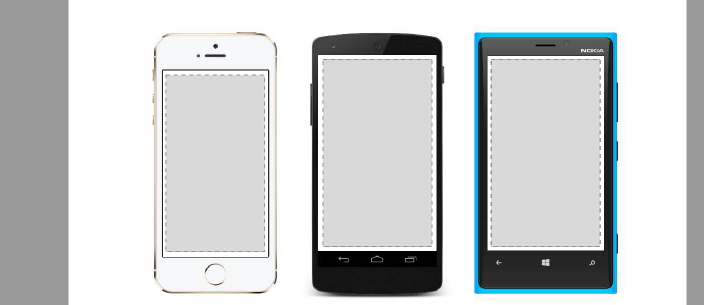
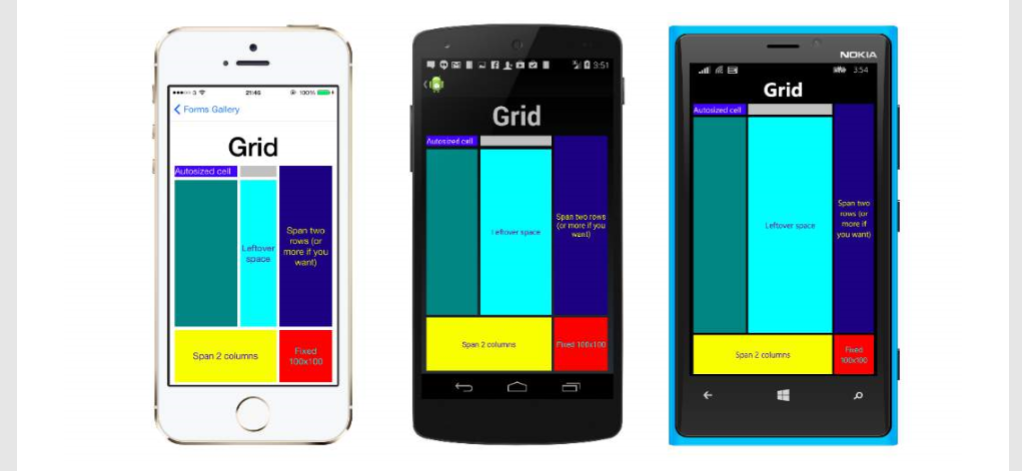
Navigation in Xamarin.Forms
NavigationPage flow with XAML App.xaml.cs file (App.xaml file is default, so skipped) using Xamrin.Forms namespace NavigationApp { public partial class App : Application { public static INavigation GlobalNavigation { get; private set; } public App() { InitializeComponent(); var rootPage = new NavigationPage(new FirstPage()); GlobalNavigation = rootPage.Navigation; MainPage = rootPage; } } } FirstPage.xaml file <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" x:Class="NavigationApp.FirstPage" Title="First page"> <ContentPage.Content> <StackLayout> <Label Text="This is the first page" /> <Button Text="Click to navigate to a new page" Clicked="GoToSecondPageButtonClicked"/> <Button Text="Click to open the new page